کتاب شاهزاده خانوم محکوم
هنگامی که شاهزادهء روس و نامزدش برای خرید لباس وارد مغازه شدند، نامزدِ شاهزاده مقابل آینه ایستاد و از فروشنده که دختری فرانسوی بود، خواست تا در پرو لباس به او کمک و از شاهزاده پرسید " لباس چه طور است؟ "
شاهزاده به آینه نگاه کرد، نگاهش به نگاه دختر فرانسوی در آینه گره خورد، دختر فرانسوی چشمانش را فورا به زمین دوخت اما شاهزاده، همانطور که به چشمان دختر فرانسوی نگاه میکرد، گفت "بسیار زیباست"

برچسبها: شخصی
WOUND REPAIR
Active TROMBIN cleaves FIBRINOGEN into FIBRIN, which polymerizes into a fibrin network (SCAB) sealing the wound
CAUSES OF TISSUE DAMAGE
Physical
Copromised blood flow
Crushing
Desiccation
Incision
Irradiation
Overcooling
Overheating
Chemical
Agent with unphysiologic PH
Agent with unphysiologic tonicity
Proteases
Vasoconstrictors
Thrombogenic agents
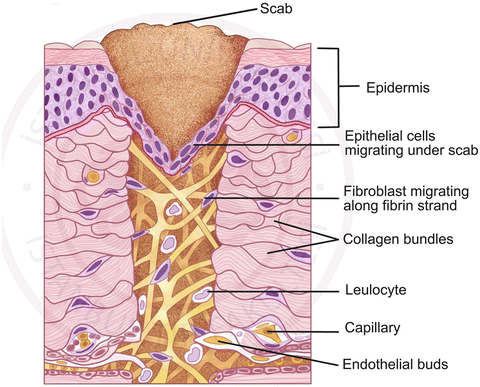
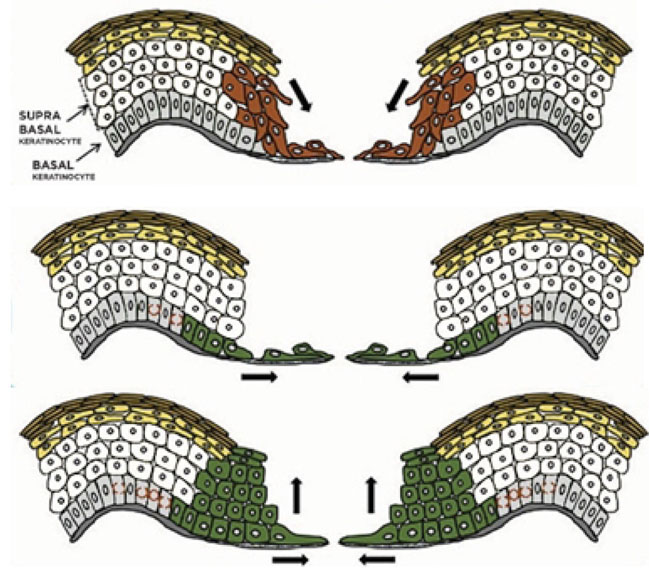
EPITHELIALIZATION
Injured epithelium has a genetically programmed regenerative ability that allows it to reestablish its integrity through proliferation, migration & a process known as contact inhibition
In general, any free edge of epithelium continues to migrate (by proliferation of germinal epithelial cells that advance the free edge forward) until it comes into contact with another free edge of epithelium, where it is signaled to stop growing laterally
Wounds in which only the surface epithelium is injured (e.g. abrasions) heal by proliferation of epithelium across the wound bed
Wounds in which the sub-epithelial tissue is also damaged proliferates across whatever vascularized tissue bed is available & stays under the portion of the superficial blood clot that desiccates (forms a scab) until it reaches another epithelial margin. Once the wound is fully epithelialized, the scab loosens and is dislodged
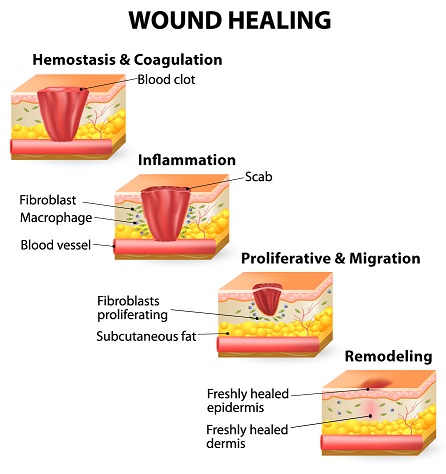
STAGES of WOUND HEALING
Inflammatory Stage
Fibroplastic Stage
Remodelling Stage
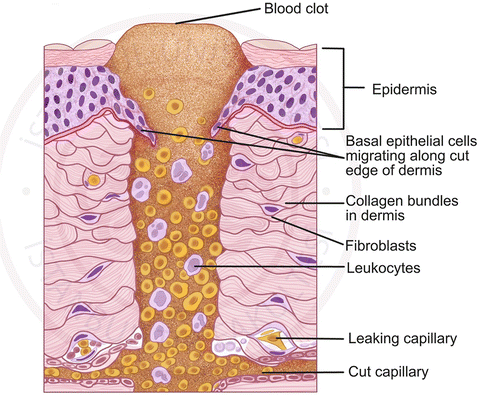
Inflammatory Stage
“Lag Phase” – the period where no significant gain in wound strength occurs.
Principal material holding together during this stage is fibrin.
Wound fills with clotted blood, inflammatory cells and plasma.
Adjacent tissue begins to migrate into wound, and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells begin to transform into fibroblast.
Immediate to 3-5 days
:(Bleeding stops (hemostasis
a. Constriction of blood supply
b. Platelets start to dot
c. Formation of scab
:Inflammation
a. Opening of blood supply
b. Cleansing of wounds
CARDINAL SIGNS OF INFLAMMATION
Redness – rubor
Swelling – tumor
Warmth – color
Pain - dolor
Loss of function
/signs-of-inflammation-4580526_FINAL-5c6f21adc9e77c0001be5177.png)
Fibroplastic Stage
Strands of fibrin, from blood coagulation, crisscross wound to form a latticework on which fibroblasts can begin laying down ground substance & tropocollagen
Occurs 5 days to 3 weeks
:Granulation
a. New collagen is laid down
b. New capillaries fill defects
:Contraction
a. Wound edges pull together
: Epithelialization
a. Cells cross over the moist surface
b. Cell travel about 3mm from point of origin
Remodelling Stage
Final stage of wound repair
Continuous indefinitely, from 3 weeks to years
Also known as “WOUND MATURATION STAGE”
Previous randomly laid down collage are destroyed & replaced by new collagen fiber of better orientation to resist tensile forces of the wound
The final process, which begins near the end of fibroplasia & continues during the early portion of remodelling, is wound contraction
During wound contraction, the edges of the wound migrate toward each other
Wound strength never reaches 80-85% of the strength of un-injured tissue
As wound metabolism lessens, vascularity is decreased, which diminishes wound erythema
...ALWAYS REMEMBER
Inflammatory Stage | Fibroplastic Stage | Remodelling Stage |
3-5 days | 5 days to 3 weeks | 3 weeks to years |
FACTORS THAT IMPAIR WOUND HEALING
Foreign Material
Necrotic Tissue
Ischemia – restriction of blood and oxygen supply
Wound Tension
Foreign Material
"Is anything that the host organism’s immune system views as “non-self
This includes bacteria, dirt, suture material, etc
Bacteria can proliferate and cause an infection in which bacterial proteins that destroys host tissue are released
Non-bacteria foreign material acts as haven for bacteria by sheltering them from host defences & thus promoting infections
Foreign material is often antigenic & can stimulate chronic inflammatory reaction that decreases fibroplasia
Necrotic Tissue
Serves as a barrier to the ingrowth of reparative cells; prolonging the inflammatory stage since the white blood cells fail to remove the necrotic debris
Serves as a protected niche for bacteria
This frequently includes blood that collects in a wound (hematoma), where it can serve as an excellent nutrient source of bacteria
:Example of Necrotic Tissue secondary to extraction*

Ischemia
(Decreased blood supply & oxygen delivery to a wound.(Black or Bluish on color
Result to further tissue necrosis - Lessen delivery of antibodies, white blood cells, and antibiotics to the wound
:Caused by
Tight or incorrectly placed sutures
Improperly designed flap
Excessive external or internal pressure on a wound
Systemic hypotension
Peripheral vascular disease
Anemia
:Example of ischemia of oral tissue*

Wound Tension
Tension from sutures cause tissue strangulation, producing ischemia
If sutures are removed too early, wound under tension may re-open resulting to excessive scar formation and wound contraction
On the other hand, when sutures are left too long, the tract where the sutures ran will epithelize then leave a permanent disfiguring mark
HEALING BY PRIMARY INTENTION
Wound edges without tissue loss are places and stabilized in essentially the same anatomic position prior to injury
Wound repair occurs with minimal scar tissue
A theoretical ideal which is difficult to attain clinically
Generally used term to designate wounds which the edges are closely reapproximated
HEALING BY SECONDARY INTENTION
Implies that a gap between edges of incision or laceration or between bone or nerve ends after repair
Tissue loss prevents close approximation of wounds edges
Requires large amount of wound repair processes
Examples are extraction sockets, deep ulcers or large avulsive injuries
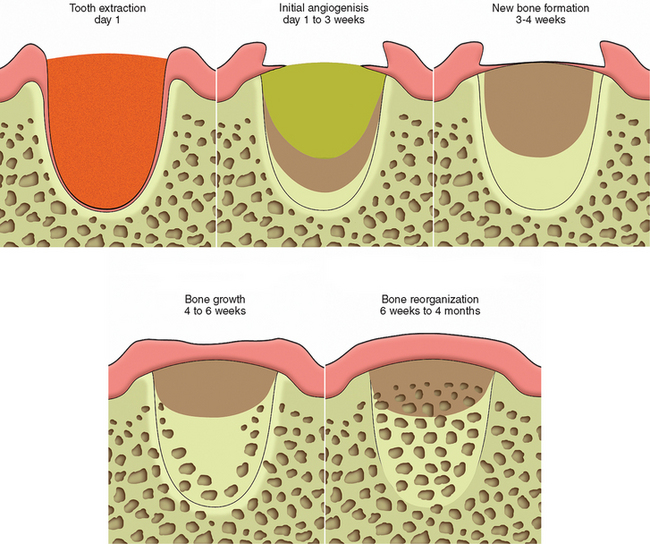
Healing of Extraction Sockets*
After extraction, the remaining empty socket consist of cortical bone (radiographically seen as the lamina dura) covered by torn periodontal ligaments, with a rim of epithelium (gingiva) at the coronal portion
The socket fills with blood, which coagulate and seals the sockets from the oral environment
:First week of healing
Inflammatory stage – White blood cells enter socket to remove contaminating bacterial & to begin break down of any debris left in the socket
Fibroplasia – ingrowth of fibroblasts and capillaries
Epithelium migrates down the socket wall until it reaches a level at which it contacts epithelium from the other side of the socket or when it encounters the bed of granulation tissue under the blood clot
Osteoclasts (Bone destroying cell) accumulate along crestal bone
:Second week of healing
Large amount of granulation tissue fill the socket
Osteoid deposition along the alveolar bone lining the socket
:Third-Fourth week of healing
Cortical bone continues to be resorbed from crest and walls of sockets
New trabecular bone is laid down across the socket
:4-6 Months
The cortical bone lining is fully resorbed, radiographically there is a complete loss of lamina dura
HEALING BY TERTIARY INTENTION
A term surgeon use to refer to wound healing through use of tissue grafts in large wounds
BONE HEALING
Bone heals by primary & secondary intention
If fracture ends are more than 1 mm or so apart, bone heals by secondary intention; wherein large amount of collagen must be laid down to bridge the bony gap
Fibroblasts and osteoblasts produce a lot of fibrous matrix such that healing tissue extends circumferentially beyond the free ends of the bone forming callus
Healing of bone by primary intentions occurs when bone is either incompletely fractured such that fracture ends does not become separated from each other,
Or when a surgeon closely re-approximates & rigidly stabilize fractured ends
In this case, little fibrous is produced & reossification of tissue within fracture area occurs quickly, with minimal callus formation
TWO FACTORS IMPORTANT TO PROPER BONE HEALING
Vascularity
If vascularity or oxygen supplies are sufficiently compromised, cartilage forms instead of bone
If either vascularity or oxygen supplies are poor, fibrous tissue does not chondrify or ossify
Immobility
Placing bone under continuous or repeated cycles of some tension stimulates continued osteoblastic bone formation
Bone is formed perpendicular to lines of tension to help withstand the forces placed on it
Excessive tension or torque placed on a healing fracture site produces mobility & compromises vascularity of the wound, promoting wound infection
IMPLANT OSTEOINTEGRATION
:Wound healing around dental implants; involves two basic factors
Healing of bone to the implant
Healing of alveolar soft tissue to the implant
HEALING OF THE BONE TO THE IMPLANT
This must occur before any soft tissue forms between the bone & the implant surfaces
:Four factors needed to achieve this
Short distance between implant & bone
Viable bone at or very near the surface of the bone along the implant
No movement of implant while bone is attaching to its surface
An implant surface free of contamination by organic or inorganic material. Including bacteria, oil, glove powder, foreign metals and foreign proteins
VIABLE BONY SURFACE ALONG THE IMPLANT
There should be minimized bone damage during site preparation to preserve the viability of the bone near implant surface
Much damage is caused by heat friction during cutting process
It is minimized by using sharp bone-cutting instruments, limiting cutting speeds to minimize frictional heat, & by keeping the bone cool with the irrigation during site preparation
Counter sinking implants & using low profile healing screws decrease chances of unwanted forces to be delivered to the implant
Covering the top of the implant during healing further protects it
?In implant, we use low-speed. Why*
Less torque to minimize damage to the bone & the healing capacity is intact
So that the drill keep on moving and penetrate the bone
FACIAL NEUROPATHY of TRAUMATIC ORIGIN
:The three branches of the trigeminal nerve injured most commonly
Inferior alveolar-mental nerve
Lingual nerve
Infraorbital nerve
types of nerve injuries
Neurapraxia
Axonotmesis
Neurotmesis
Neurapraxia
Least severe form of peripheral nerve injury
Contusion of a nerve in which continuity of the epineurial sheath and the axons is maintained
Blunt trauma or traction (e.g., stretching) of a nerve, inflammation around a nerve, or local ischemia of a nerve
No loss in axonal continuity, spontaneous full recovery of nerve function usually occurs in a few days or weeks
Axonotmesis
When the continuity of the axons but not the epineurial sheath is disrupted
Severe blunt trauma, nerve crushing, or extreme traction of a nerve
Because the epineural sheath is still intact, axonal regeneration can (but does not always) occur with a resolution of nerve dysfunction in 2 to 6 months
Neurotmesis
Most severe type of nerve injury
Complete loss of nerve continuity
Produced by badly displaced fractures, severance by bullets or knives during an assault, or by iatrogenic transection
Prognosis is poor except if the ends of the affected nerve have somehow been left in approximation and properly oriented
(NERVE HEALING (Two phases
Degeneration
a. Segmented demyelination
b. Wallerian degeneration
Regeneration
Segmented Demyelination
Myelin sheath is dissolved in isolated segments
This causes a slowing of conduction velocity and may prevent the transmission of some nerve impulses
:Symptoms
a. Paresthesia -a spontaneous and subjective altered sensation that a patient does not find painful
b. Dysesthesia -a spontaneous and subjective altered sensation that a patient finds uncomfortable
c. Hyperesthesia -excessive sensitivity of a nerve to stimulation
d. Hypoesthesia -decreased sensitivity of a nerve to stimulation
Occur after neurapraxic injuries or with vascular or connective tissue disorders*
Wallerian degeneration
Axons and myelin sheath of the nerve distal to the site of nerve trunk interruption' (away from the central nervous system) undergo disintegration in their entirety
Stops all nerve conduction distal to the proximal axonal stump
Occurs after nerve transection and other destructive processes that affect peripheral nerves
occurring after nerve trauma*
Regeneration
Normally the proximal nerve stump sends out a group of new fibers (the growth cone) that grow down the remnant Schwann cell tube
Growth progresses at a rate of 1 to 1 .5 mm/d and continues until the site innervated by the nerve is reached or growth is blocked by fibrous connective tissue or bone
Begin almost immediately after nerve injury*
Reference:
Lecture of Dr Reece Aldrin Valdez at national university college of dentistry- manila, philippines

برچسبها: Surgery
تا که بودیم نبودیم کسی، کُشت مارا غم بی همنفسی
تا که رفتیم همه یـــــار شدند، خفته ایم و همه بیــــدار شدند
قدر آئینه بدانیم چو هست، نه در آن وقت که افتاد و شکست
درحیرتم از مرام این مردم پست، این طایفه ی زنده کش مُرده پرست
تا هست به ذلت بکشندش به جفا، تا رفت به عزت ببرندش سر دست
آه میترسم شبی رسوا شوم، بدتر از رسواییم تنها شوم
آه از آن تیر و از آن روی کمند، پیش رویم خنده پشتم پوزخند
شعر: تا که بودیم نبودیم کسی اثر اقبال لاهوری
نقاشی: آفرینش آدم اثر میکل آنژ Michelangelo The Creation of Adam

برچسبها: شخصی
کتاب هاکلبری فین
زندگی در خانه خیلی خوب است، اما در قایق احساس آزادی و راحتی بیشتری می کنی.

برچسبها: شخصی
آیا ما قبلاً یکدیگر را ندیده ایم؟ جایی در یک موسیقی ؟
نقاشی: رقص با موسیقی زمان اثر نیکولاس پوسن Nicolas Poussin A Dance To The Music Of Time

برچسبها: شخصی
من همه را میبینم اما، تو را نگاه مینم
نقاشی: عاشق تاج گذاری کرد اثر ژان هونوره فراگونارد Honoré Fragonard The lover crowned

برچسبها: شخصی
هرکه با من همره و پیمانه شد، عاقبت شیدا دل و دیوانه شد
قصهام عشاق را دلخون کند، عاقبت خواننده را مجنون کند
آتش عشق ست و گیرد در کسی، کاو، ز سوز عشق میسوزد بسی...
شعر: قصه رنگ پریده اثر نیما یوشیج
نقاشی: جیغ اثر ادوارد مونیک Edvard Munch The Scream

برچسبها: شخصی
زندگی آوازی است که به جان ها جاری است
زندگی نغمه سازی است که در دست نوازشگر ما است
زندگی خواب خوش کودک احساس من است
زندگی جاده و راهی است به آن سوی خیال
زندگی برف سپیدی است که بر روح تو بنشسته به شب
زندگی بوی خوش نسترن است
زندگی رفتن خاموش به یک تنهایی است
زندگی رفتن و از بودن خود دور شدن است
شعر: زندگی رفتن و راهی شدن است اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاشی: طوفان در دریای جلیل اثر رامبرانت هارمنزون فان راین Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn The Storm on the Sea of Galilee

برچسبها: شخصی
حیلت رها کن عاشقــا، دیوانه شو، دیوانه شو
و انـدر دل آتش درآ، پــــروانـه شــو، پروانــــــه شو
هــم خــویش را بیگـــانه کن، هم خانه را ویرانه کن
و آنگه بیا با عاشقان، هم خانـه شـو، هم خانه شــو
رو سینــه را چـون سینه ها، هفت آب شو از کینه ها
و آنگـــه شراب عشــق را پیمانـــه شــــو پیمانــه شـو
باید کـــه جملــه جــان شــوی،تا لایق جانان شوی
گـــر ســوی مستــان میــروی، مستانه شـــو، مستانه شو
شعر: دیوان شمس اثر مولوی
نقاشی: دوشیزگان رومی اثر لونا داماس Luna Damas Romanas

برچسبها: شخصی
زندگی رسم خویشاوندی است
زندگی بال و پری دارد با وسعت مرگ
پرسشی دارد اندازه ی عشق
زندگی چیزی نیست که لب طاقچه ی عادت از یاد من و تو برود
زندگی حس غریبی است که یک مرغ مهاجر دارد
زندگی سوت قطاری است که در خواب پلی می پیچد
شعر: زندگی رسم خوش آیندی است اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاشی: تاب اثر ژان هونوره فراگونارد Honoré Fragonard The Swing

برچسبها: شخصی
در میان این همه غوغا و شر، عشق یعنی کاهش رنج بشر
عشق یعنی گل به جای خار باش، پل به جای این همه دیوار باش
عشق یعنی تشنه ای خود نیز اگر، واگذاری آب را، بر تشنه تر
عشق یعنی دشت گل کاری شده، در کویری چشمه ای جاری شده
عشق یعنی ترش را شیرین کنی، عشق یعنی نیش را نوشین کنی
هر کجا عشق آید و ساکن شود، هر چه نا ممکن بود ، ممکن شود
شعر: عشق چیست اثر مجتبی کاشانی (سالک)
نقاشی: رقص در مولن دُلا گالت اثر پیر آگوست رنوار Pierre-Auguste Renoir Dance at Le moulin de la Galette

برچسبها: شخصی
به آسانی مرا از من ربودی، درون کوره ی غم آزمودی
دلت آخر به سرگردانیم سوخت، نگاهم را به زیبایی گشودی
!بسی گفتند: دل از عشق برگیر! که نیرنگ است و افسون است و جادوست
!ولی ما دل به او بستیم و دیدیم: که این زهر است ، اما…نوشداروست
چه غم دارم که این زهر تب آلود، تنم را در جدایی می گدازد
از آن شادم که در هنگامه درد، غمی شیرین دلم را می نوازد
شعر: زهر شیرین از فریدون موشیری
Honoré Fragonard Progress of Love نقاشی: پیشرفت عشق اثر ژان هونوره فراگونارد

برچسبها: شخصی
چترها را باید بست، زیر باران باید رفت
فکر را، خاطره را، زیر باران باید برد
با همه مردم شهر ، زیر باران باید رفت
دوست را، زیر باران باید دید
عشق را، زیر باران باید جست
زیر باران باید با زن خوابید
زیر باران باید بازی کرد
زیر باران باید چیز نوشت،حرف زد،نیلوفر کاشت
زندگی تر شدن پی در پی
زندگی آب تنی کردن در حوضچه اکنون است.
رخت ها را بکنیم،آب در یک قدمی است،روشنی را بچشیم
شب یک دهکده را وزن کنیم، خواب یک آهو را، گرمی لانه لک لک را ادراک کنیم
شعر: چترها را باید بست اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاشی: پاریس، یک روز بارانی اثر گوستاو کایبوت Gustave Caillebotte Paris Street-Rainy Day

برچسبها: شخصی
نیست رنگی که بگوید با من: اندکی صبر ، سحر نزدیک است
هردم این بانگ برآرم از دل : وای ، این شب چقدر تاریک است!
خنده ای کو که به دل انگیزم؟ قطره ای کو که به دریا ریزم؟ صخره ای کو که بدان آویزم؟
مثل این است که شب نمناک است
دیگران را هم غم هست به دل
غم من ، لیک، غمی غمناک است
شعر: مرگ رنک اثرسهراب سپهری
نقاشی: منظرهای از تولدو اثر اِل گِرکو El Greco View of Toledo

برچسبها: شخصی
کودکان احساس! جای بازی اینجاست
زندگی خالی نیست
مهربانی هست، سیب هست، ایمان هست
آری تا شقایق هست زندگی باید کرد
در دل من چیزی است مثل یک بیشه نور، مثل خواب دم صبح
و چنان بی تابم که دلم می خواهد
بدوم تا ته دشت، بروم تا سر کوه
دورها آوایی است که مرا می خواند
شاید آن روز که سهراب نوشت : تا شقایق هست زندگی باید کرد
خبری از دل پر درد گل یاس نداشت،باید اینجور نوشت:
هر گلی هم باشی چه شقایق چه گل پیچک و یاس، زندگی اجباریست!
شعر: تا شقایق هست زندگی باید کرد اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاشی: منظره زمستانی با یک پرنده اثر پیتر بروگل Pieter Bruegel Winter Landscape with Skaters and Bird Trap

برچسبها: شخصی
ابری نیست
بادی نیست
می نشینم لب حوض
گردش ماهی ها، روشنی،من، گل، آب
نردبان از سر دیوار بلند، صبح را روی زمین می آرد
روزنی دارد دیوار زمان، که از آن،چهره من پیداست
می روم بالا تا اوج،من پر از بال و پرم
راه می بینم در ظلمت، من پر از فانوسم
من پر از نورم و شن
و پر از دار و درخت
پرم از راه، از پل، از رود، از موج
پرم از سایه برگی در آب، چه درونم تنهاست!
شعر: روشنی من گل آب اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاشی: گاری علوفه اثر جان کانستبل John Constable Hay Wain

برچسبها: شخصی
هیچ حیوانی به حیوانی نمی دارد روا
آنچه این نامردان با جان انسان میکنند
صحبت از پژمردن یک برگ نیست
فرض کن مرگ قناری در قفس هم مرگ نیست
فرض کن یک شاخه گل هم در جهان هرگز نرست
فرض کن جنگل بیابان بود از روز نخست
در کویری سوت و کور، در میان مردمی با این مصیبت ها صبور
صحبت از مرگ محبت مرگ عشق، گفتگو از مرگ انسانیت است
شعر: وای جنگل را بیابان میکنند اثر فریدون مشیری
نفاشی: سوم ماه مه فرانسیسکو گویا Francisco Goya The third may

برچسبها: شخصی
چه کسی میداند؟
که تو در پیله ی تنهایی خود، تنهــــایی؟
چه کسی می داند که تو در حسرت یک روزنه در فردایــی؟
پیله ات را بگشا،تو به اندازه ی پروانه شدن زیبایی!
شعر: آرزوها اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاشی: ژوئن سوزان اثر فردریک لورد Frederic Lord Leighton Flaming June

برچسبها: شخصی
من اینجا ریشه در خاکم
من اینجا عاشق این خاک اگر آلوده یا پاکم
من اینجا تا نفس باقیست می مانم
من از اینجا چه می خواهم، نمی دانم
امید روشنائی گر چه در این تیره گیهانیست
من اینجا باز در این دشت خشک تشنه می رانم
من اینجا روزی آخر از دل این خاک با دست تهی
گل بر می افشانم
من اینجا روزی آخر از ستیغ کوه چون خورشید
سرود فتح می خوانم
شعر: ریشه در خاک اثر فریدون مشیری
نقاشی: سرگردان بر فراز دریای مه اثر کاسپر دیوید فریدریش Caspar David Friedrich Wanderer above the Sea of Fog

برچسبها: شخصی
گفت دانایی که: گرگی خیره سر
!هست پنهان در نهاد هر بشر
لاجرم جاری است پیکاری سترگ
روز و شب، مابین این انسان و گرگ
زورِ بازو ، چاره ی این گرگ نیست
صاحب اندیشه داند چاره چیست
هر که گرگش را در اندازد به خاک
رفته رفته می شود انسان پاک
و آنکه از گرگش خورد هردم شکست
گرچه انسان می نماید گرگ هست
و آن که با گرگش مدارا می کند
خلق و خوی گرگ پیدا می کند
!در جوانی جان گرگت را بگیر
وای اگر این گرگ گردد با تو پیر
مردمان،گر یکدگر را می درند
گرگ هاشان رهنما و رهبرند
شعر: گرگ درون اثر فریدون مشیری
Peter Paul Rubens Massacre of the Innocents نقاشی: کشتار بیگناهان اثر پیتر پاول روبنز

برچسبها: شخصی
قايقي خواهم ساخت، خواهم انداخت به آب
دور خواهم شد از اين خاک غريب
همچنان خواهم راند. همچنان خواهم خواند: دور بايد شد، دور
شب سرودش را خواند، نوبت پنجرههاست
همچنان خواهم خواند, همچنان خواهم راند
پشت دریاها شهری است, كه در آن پنجرهها رو به تجلی باز است
مردم شهر به یک چينه چنان مينگرند, كه به یک شعله، به یک خواب لطيف
خاک، موسيقی احساس تو را ميشنود
و صدای پر مرغان اساطير میآيد در باد
پشت درياها شهری است
كه در آن وسعت خورشيد به اندازه ی چشمان سحرخيزان است
شاعران وارث آب و خرد و روشنی اند
پشت درياها شهری است
قايقی بايد ساخت
شعر: پشت دریاها اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاسی: موج نهم اثر ایوان آیوازوفسکی Ivan Aivazovsky Ninth Wave

برچسبها: شخصی
دی شیخ با چراغ همیگشت گرد شهر
کز دیو و دد ملولم و انسانم آرزوست
شعر: دیوان شمس اثر مولوی
نقاشی: تراس کافه در شب اثر ونسان ونگوگ Vincent van Gogh Café Terrace at Night

برچسبها: شخصی
صدا کن مرا, صدای تو خوب است
صدای تو سبزینه آن گیاه عجیبی است, که در انتهای صمیمیت حزن می روید
در ابعاد این عصر خاموش, من از طعم تصنیف درمتن ادراک یک کوچه تنهاترم
بیا تابرایت بگویم چه اندازه تنهایی من بزرگ است, و تنهایی من شبیخون حجم ترا پیش بینی نمی کرد
و خاصیت عشق این است, کسی نیست
بیا زندگی را بدزدیم آن وقت, میان دو دیدار قسمت کنیم
بیا با هم از حالت سنگ چیزی بفهمیم, بیا زودتر چیزها را ببینیم
بیا آب شو مثل یک واژه در سطر خاموشی ام, بیا ذوب کن در کف دست من جرم نورانی عشق را
مرا گرم کن
شعر: صدا كن مرا. صداي تو خوب است اثر سهراب سپهری
نقاشی : شب پرستاره اثر ونسان ونگوگ Vincent van Gogh Starry Night

برچسبها: شخصی
من اينجا بس دلم تنگست
و هر سازی که میبينم بدآهنگست.
بيا رهتوشه برداريم،
قدم در راه بیبرگشت بگذاريم،
ببينيم آسمانِ "هر کجا" آيا همين رنگست؟
شعر: من اینجا بس دلم تنگ است اثر مهدی اخوان ثالث
نقاشی: خش خش باران اثر لئونید آفرمو Leonid Afremov Rain’s Rustle

برچسبها: شخصی
Endodontics Notes
*Cardial sign of inflammation & their causes:
Dolor = pain
Calor = heat
Tumor = swelling
Rabor = redness
Functionalsia = loss of function
*First is vasodilation followed by vasoconstriction (anterior constriction); the sequence:
↑ blood flow
↑ vascular permeability
Enema / Exaduation
Escape of Leukocytes of sites of injury
necrosis
*Types of inflammation:
1. Chronic : long - Macrophages
2. Acute : suddenly - Neutophils
*Causes of pulpal inflammation:
1.Bacterial (most common cause)
2.Physical
3.Chemical
4.Idiopathic
1. Bacterial (mostly streptococcus mutans)
At Coronal (crown) & Radical (root) cause caries which leads to :
Fracture (complete or incomplete)
Non-fracture trauma (weakness due to pathologic)
once there is caries or fracture on crown which provide an opening or passage for bacteria to reach the apex & by disturbuting of infection cause widdening of periodomtal space & breakage of lamina dure & formation of sinus tract & in advance result toinflammation at lymph nodes:
Parotid gland = stensen's duct
Sublingual gland = Bartholin's duct
Submandibular gland = Wharton's duct
At Anomalous tract :
Tubercle or protuberance from the involved surface thats shows extra bump or cusp.
originates from the central groove or lingual ridge.
Dens invaginatus : incisor, most common is max lateral.
Dens envaginatus : Premolars & molars, most common is mandibular premolars.

At Radiation
Retrogenic infection through:
Periodontal inflammtion & calcular deposite cause 1.periodontal disease(gum recession) 2.periodontal pocket 3.periodontal abscess
Blood cause hematogenic (pertaining to the formation of blood or blood cells).
Saliva cause periodontal cancer by radiotion therapy.
bacteria has 2 way to reach apex: 1.pulp 2.periodontal ligument
2. Physical
Acute:
Sudden Fracture by 1.coronal 2. radiation
Vascular stasis during correction of orthodontic problem by forces that apply to the tooth.
Luxation (labial/buccal or lingual movement) & Avulsion (tooth suddenly lock out of socket)
Chronic:
Adolescent
Female Bruxism that leads to 1.Abrasion 2.Malocclusion 3.TMJ problem 4.Truma to periodontium 5.Pulp exposure
Attrition (physiological) /Abrasion (mechanical)
Erosion (chemical)
3. Chemical
Filiing material
cement:
IRM (Internative & Restorative material; Disadvantages is Expensive)
GIC (Flouride release that stop formation of caries)
Zinc Oxide Eugenol (Temporary cement that Promote tertiary dentin)
Polycarboxylate (True adhesion to tooth structure as a base or lutting cement when the cavity preparation is close to the pulp;The powder is zinc oxide & liquid is polyacrylic acid or a copolymer of that acid; Disadvantages are low tensile strength & no fluoride release & intraoral solubility)
Zinc phosphate (Never use in vital teeth because it contain acid & can irrigant the pulp)
Plastic:
Polymeric resins (use in restoring & replacing tooth structure or missing teeth that can be bonded with other resins or directly to tooth structure or to other restorative materials such as amalgam; Polymer is the liquid & Monomer is powder. Examples: Self cure resin & Heat cure resin)
Composite resin resotorative fillings (Because of the resin mimics has the appearance of natural teeth that also known as “white fillings” or “tooth-colored fillings")
Etching agent:
Removes smear layer & wet of the enamel to promote adhesion. 35% phosphoric acid for 15 seconds & wash well the tooth with water & dry after use
Cavity liners:
Cavity warnish for Amg
Bonding agent for composite
curing times is 20 sec
Alcohol/ether:
Cavity base that provides protection
Calcium hydeoxide (Dycal)
GIC type I (Luting cement for cementation of crown & bridges), type II (Restorative)
Disinfectant
AgNo3 (silver nitrate)
Phenol (using during pulpotomy)
NaFl (sodium fluorescein)
4. Iatrogenic
Cause by dentist druring:
Cavity prepration by Expose the pulp.
Restoration by wrong pack (No space between filling material).
Intentional extripation (ریشه کنی و نابئدی عمدی) by Exposing pulp tissue.
Orthodontic movement by forces that apply to the tooth.
Periodontal curettage by Severe mobility of tooth
Electrosurgery by Laser burns
Periapical curettage
Osteotomy by Cutting the bone.
Intubation by strike the teeth as it's rapidly and forcefully passed through the mouth and cause chipped teeth.

*Idiopathic - None cause:
Aging
Internal resorption

External reorption
Hypophosphatasia
Effect bone formation & disturbe mineralization
Sickle cell anemia
Hematogenic disease that decrease RBC so ↑ risk of infection.
*Pathogenesis:
1st ↓dentin permeability that leads to dentin sclerosis (hardening of dentin)
2nd formation of new dentin (secondary dentin)
3rd inflammatory & immune reaction (hyperemia) that leads to pulpitis then necrosis.
*Disease of the pulp :
1. Hyperemia
Physiologic term for inflammation.
↑ blood flow of pulp tissue.
Different with pulpitis.
Significance is 1st sign of pulp in stress.
Because of presence of causes (bacteria, trauma,...) that leads to Hypercemia (vasodilation followed by vasoconstriction) which finally result to Pulpitis.
2. Pulpitis
inflammation of pulp can be:
Acute/Chronic
Partial(some part of pulp expose) / Total (all part of pulp expose)
Infected (pus/abscess) / Sterile (no pus)
*Types of Pulpitis:
Inflammatory (Reversible & Irreversible)
Pulp Degeneration (calcific & Atrophic & Fibrous & Pulpartifacts & Tumors)
Necrosis
Inflammatory
Reversible
Mild to moderate inflammation of pulp because of noxious stimuli.
Px complain of pain that produced by thermal (hot & cold) stimuli.
Capable to retaining to uninflamed state by removal of stimuli.
Pain of brief duration produced by thermal stimuli.
Pain subside as soon as stimuli removed.
Sharp pain for few second or moment. (dentinal tubules is exposed)
Symptomes by cold food or cold air.
No accur spontaneously, its reactive.
No continue to accour when cause removed.
Thernal response are momentary, quick, sharp, hypersensitive response, subsides as soon as stimulus removed.
Percussion & Palpation is Negative.
in X-ray :
Caries not reach the pulp. (only in enamel or dentin)
No radiolucency at apex.
No widdening of periodontal space
Lamina dura is intact - continious & radiopaque (lamina dura is thin bone occupize periodontal space but if there is break ,No contact)
Tx of reversible:
Early detectable & removal of cause.
Retreatment of cure.
prepare wet cavity & proper utilization chemical drug & restorative procedure.
Never desicate dentin during restorative procedure.
Outcome of treated reversible:
Favorable if irritant is removed early enough; if not detectable & treate on time, will continue & develop into irreversible.
Irreversible
Persistant inflammatory condition of pulp cause by Noxious stimulus.
Can be Symptomatic (pain) or Asymptomatic (no pain)
Can be Acute or Chronic.
Can be with Pus (infected) or No pus (sterile)
Progression of reversible pulpitis.
Pain caused by hot/cold stimulus.
Pain man accour spontaneously.
Pain persist for several min to hour.
Lingering after removal of thermal stimuli (Can ot go back to normal)
Hemorrhage & pain during probing.
In X-ray:
Deep cavity extending to pulp or decay under filling.
Caries exposed pulp or envolved surface of pulp.
Tx irreversible:
Emeregency tx is pulpectomy & placing material such as Formocresol (has too much formalin cause bone resoption)
Root canal tx
Extracted if its not restorable
Outcome of treated irreversible:
Favorable after proper endodontic procedure is done with proper restoration of tooth; if not detectable & treate on time, will continue & develop into necrosis.
Types of irreversible:
1. Acute
Short duration
Abnormally response tp cold/heat
Caries:
Smooth surface (labial, buccal, lingual, proximal)
Pit & Fissure&occlusal (lingual pit of max 1st molar, Buccal pit of mand molar, incisors)
Radiographic:
Deep caries with apparent pulpal exposure, extensive restoration
Theckening of periodontal space (advance stage)
Symptomatic:
Moderate-severe spomtaneous(accour naturally)
Inter mittent(on&off) or continous, sharp, dull
Radiating(not local,can go to neck) or Reffered(can not determined location), difficult to localize.
Intense pulsating type which becomes intermittent & throbbing
Contious for long period & worse when heat is applied
Pain relieved by application of heat/cold
Affect by postiral change(at night, sleep); Sleep with elevated head(seatin position)
Types of acute:
Suparative pulpitis presence of pus
Serous Pulpitis Extensive carise with No pulp expusure; Mild pain & increase sensivity during hot/cold test, sprecially hot test & negative to percussion
2. Chronic:
Asympotomatic
With pulp exposure
Hyperplastic pulpitis
Internal resorption
Types of chronic:
Chronic Close pulpitis No gross cavity & slowing advamcing caries
Chronic open pulpitis Big caries involvement
1. Ulcerative
expose the pulp & may favorable if symptomes relieved
2. Hyperplastic
Other name is pulp polyp
Chronic proliferative pulpitis, productive inflammation(hyperplasia) of pulp to extensive caries exposure of young pulp.
Characterized by development of granulation tissure that covered with epithelium; in otherword Granuloma with stratified squamous epithelium lined with polymorphous cell.
Clinical appearance is Fleshy reddish pulp that filled pulp chamber.
Resulting from long standing low grade irritation of pulp.
In young px & adult, no more above 50 y.o
Pain is not common unless disterbuted, painfull during presence of food & sensitive to hot/cold.
Tx is cut the pulp with spoonshape & excavation then RCT.
Outcome is favorable after endo tx or resto & can be unfavorable if left withouy tx.
X-ray of pulp polyp shows big radiolucency with direct access to pulp chamber.
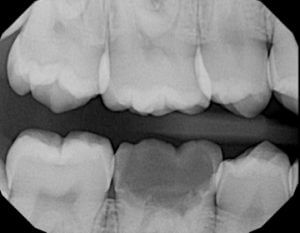
*Pulp inflammation overview
1. pulp hyperemia
If does not treat will lead to Reveressible
2. Reversible pulpitis
If does not treat will lead to Irreveressible
3. Irreversible pulpitis
3.1. Actue Irreversible pulpitis
3.1.a. Acute Suparative pulpitis
3.1.b. Acute Serous pulpitis
3.2. Chronic Iireversible Pulpitis
3.2.a. Chronic Close pulpitis
3.2.a.b. Chronic Open Pulpitis
3.2.a.b.a. Chronic ulcerative Open Pulpitis
3.2.a.b.b. Chronic huperplastic Open Pulpitis
If does not treat will lead to Necrosis
4. Necrosis
4.1. Liquifactive necrotic pulp
4.2. Coagulative necrotic pulp
4.2.a. Caseation Coagulative necrotic pulp
Reversible | Irreversible |
Pain transient(short duration) & lasting in matter of second | Pain Continue after removal of stimulus & lasting for several month or longer |
Percussion negative | Percussion positive |
Mobility no | Mobility May or may not |
Sensitive cold | Sensitive hot/cold & sweet |
Necrosis
Common condition affecting tooth which pulp killed by Acute or Chronic inflammation.
History of pain that disappear.
Pulp extripation on tooth extraction is necessary.
Pulp Death that cause reduction of pain of tooth because all the tooth's nerves are in pulp, by death of pulp the px can feel the pain any more
Death of pulp can be partial or total.
sequel of inflammation of pulp following a traumatic injury:
1. Pulp is destroyed before inflammatory reaction takes place.
2. Ischemic infarction causing Dry-gangreous necrotic pulp whicj is blackage or bluish discoloration is most common cause by trauma.
3. Liquifactive, proleolytic enzyme convert pulp tissue into softtened mass that results liquid amorphous debris.
3. Coagulative necrotic, soluble portion of tissue is precipitated or converted into solid material.
4. Caseation is form of Coagulative necrotic, tissue converted to chessy mass consisting chiefly of Coagulated protein, fat, water.
End product of pulp decomposition is Hydrogen sulfide, Ammunis, Fleshy substance, Indican, Ptomaines, water, carbon dioxide.
Intermediate products contribute to unpleasant odor emanting from root of canal.
*Periapical Abscess
Result of decay & infection extending into pulp of tooth.
Break in periodontal ligument provide passage of bacteria toward the apex.
pain is severe, persistant, throbbing.
Tooth is tender to touch if not treted pus.
Tx:
Incision-dranaige of pus & Antibiotic therapy (Amoxicillin 500mg, Dispence # of antibiotic with type of anitbiotic either capsule or tablet, instruction take one capsule 3 times aday)
Root canal therapy
Extraction
*Periapical Granuloma:
Other name is Acute Periodontitis.
One of the most common sequel of pulpitis
Localized mass of chronic granulation tissue formed due to infection.
Hyperemia, Edeme, Inflammation of apical periodontal ligument.
X-ray:
Thickening of periodontal space
Root canal at apex is circumscribed.
*Osteomyelitis:
Inflammation of bone & bone marrow
Result of Odontogenic infection that develops to the Jaw.
Reference:
Lecture of Dr annalie De Lemos at national university college of dentistry-manila philippines
برچسبها: Endodonthics
Anesthesis summery
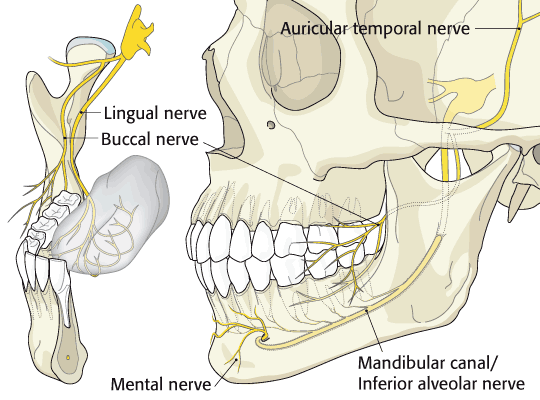
A.Trigeminal nerve (Cranial nerve V) devision:
1.Ophthalmic (V1)
2.Maxillary (V2)
3.Mandibular (V3)
*sensory: To skin of the face, Nose & nasal cavity, Forehead, Temple, Teeth, Tongue, Palate .( involve V1,V2,V3)
*motor: To muscle of mastication & Anterior belly of digastric & Masseter.(only V3)
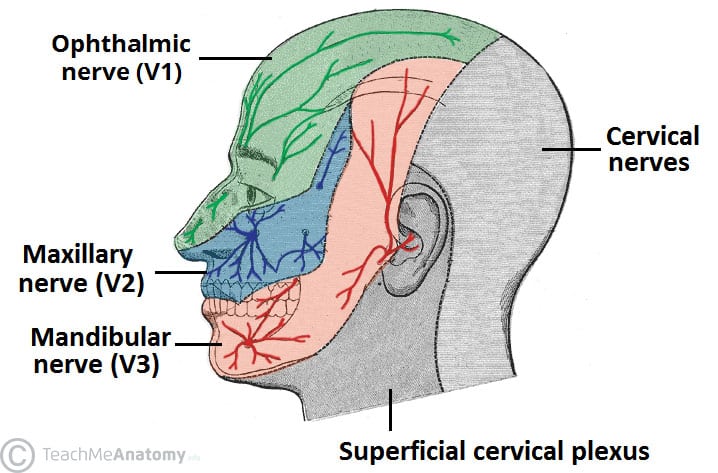
1. Ophthalmic (V1 ):

2. Maxillary (V2 ):
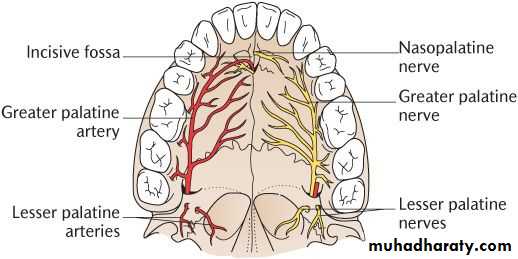
*Nasopalatine: Lower posterior nasal septum, Mucous membrane of anterior hard palate.
*Greater palatine: Mocous membrane of posterior hard palate.
*Lesser palatine: Soft palate of tonsils
*Superior Alveolar Nerves:
Anterior Superior Alveolar Nerves (ASAN): Anterior teeth & Maxillary sinus
Middle Superior Alveolar Nerves (MSAN): Premolars & MB root of 1st molar & maxillary sinus
Posterior Superior Alveolar Nerves (PSAN): DB and palatal root of 1st molar , 2nd molar , 3rd molar , Maxillary sinus
3. Mandibular (V3) :
*Lingual nerve: Anterior two third of the tongue, Lingual gland, Submandibular gland, Sublingual gland.
*Buccal nerve: Cheek, Buccal gingiva of lower molars
* Inferior Alveolar nerve (IAN): goes into the mandibular foramen
Dental nerve: Lower molars & Premolars
Mental nerve: Skin of lower lip & Chin (exits the mental foramen)
Incisive nerve: Lower Incisor & Canines
*Temporal nerve
*Lateral pterygoid nerve
*Medial pterygoid nerve
B.contraindicated:
*when there is infection or inflammation in the area of the injection site.
*when there is presence of pus because pus is Acidic and anesthesia is Base so its does not work & aside from that is too much painful, so aspirate &treat the pust before anesthesia.
*when the health of px is compromised.
C. Maximum Recomendation Dose:
*Maximum amount of carpules that can be use in a person at a time is 10 carpules.
*Using different types of carpules a person at a time can cause Anaphylactic shock.
*Choose the Anesthetic Drug base on px health condition; For example Never use Lidocaine for Asthma px causeit can increasing heart rate ,use Aritrocainre Or Never use Lidocaine for hyperthroid px cause it leads to anfractuous, use articaine.

D. Dosage Calculation:
*Formulla: Maximum Recomendation Dose ✖ Body Weight= Total ÷ Amount of lidocaine in 1 carpule
*Example: 20 kgr child can tolerate how many carpule of 2% lidocaine with vasoconstrictor?
For "Amount of lidocaine in 1 carpule" read the written information on the carpules that you bought (depends on the carpule brands)
Usually in 1 carpule 1.8 mL of 2% lidocaine is used.
2% lidocaine is equal to 20 mg/ml
So Amount of lidocaine in 1 carpule = 20 mg/mL ✖ 1.8 mL= 36 mg/carpule
Maximum Recomendation Dose ✖ Body Weight= Total ÷ Amount of lidocaine in 1 carpule
4.4 mg/kg ✖ 20 kg = 88 mg ÷ 36 mg/carpule = 2.4 carpules
It means to say for 20 kg child, you can use two & half carpules.
E. Local Anesthetic Drug Information:
*Most common used: 2% Lidocaine with vasoconsrictor 1:100 000 Epinephrine
*Epinephrine as vasoconstrictor increase pulse rate
*Before using the cartridge, sterile with 70% alcohol & wash with body temprature water.
*Place the carpule at Hot water for 5min for better control of the pain produced during the administration of dental anesthesia injection; because Heat can cause the lidocaine to be absorbed into your body faster .

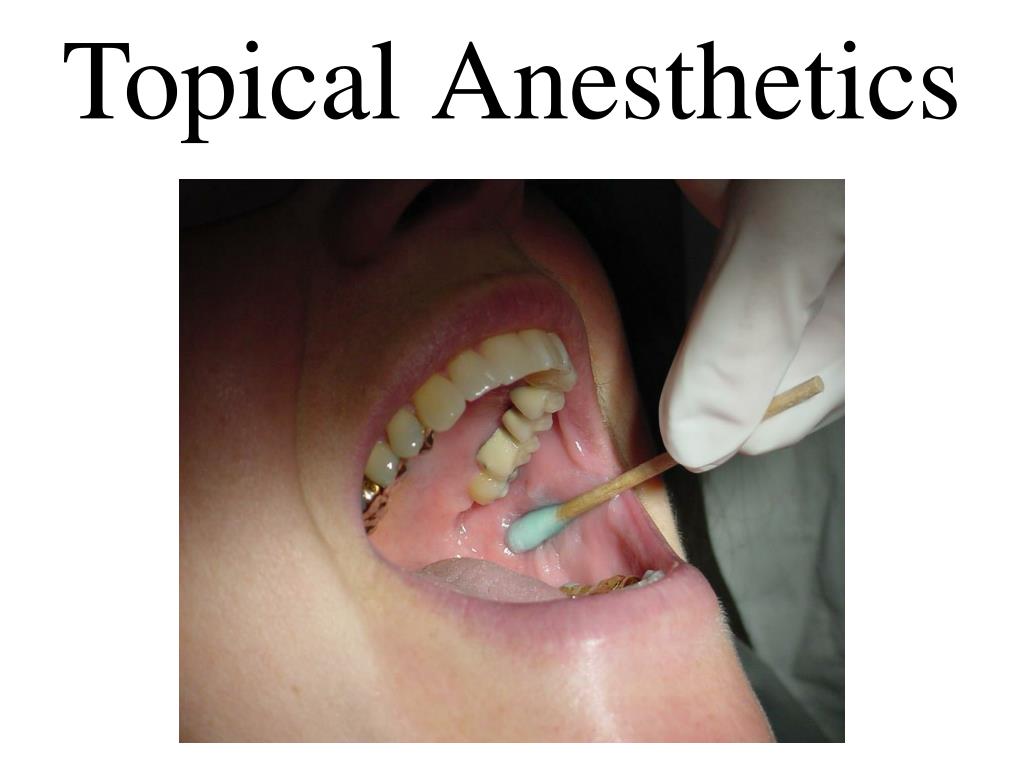
F. Topical anesthesitic:
Identify the landmarks by palpation & dry the area
Apply topical anesthetic Gel 20% Benzocaine. The Onset is 20 sec & recommended applying for 1-2 min & effecting time is 5-15 min.
Once the color of tissue change to white means " Blanching" that shows tissue numbness.
G. Needle:
As increasing # gauge we have decreasing of needle diameter
The most common gauges are 25, 27, and 30 gauge.
27 gauge, the smallest gauge -largest diameter) is highly suggested Because the diameter is small so it will not be painful for patient & easy aspiration but has enogh strength to penetrate the tissue without deflection.
Long needle is about 32 mm (1.5 inches) and the short needle is about 20 mm (1.0 inch).
Bevel of the needle shoud face the cortical bone.
H. Aspiration & Deposite:
*Syringe should contain No air.
*Always make sure that you are heat the bone then, withdraw the needle 1mm
*Aspirate for 20 sec must be negativeTo make you sure that you will deposite in the nerve not in the blood vessels & if after aspiration you see the blood it means its positive & you must correct your needle position base on landmarkes
*After Aspiration, Deposite slowly in 60 sec ;To avoid pain and ulceration.
*Once you insert the needle ask the px to Inhale.
*Once you deposite the carpule ask the px to Exhale.
*Always Slowly remove the needle & palpate the area to help disturbution of anesthesia.
*Wait for 2-3 min to act.
H. Techniques:
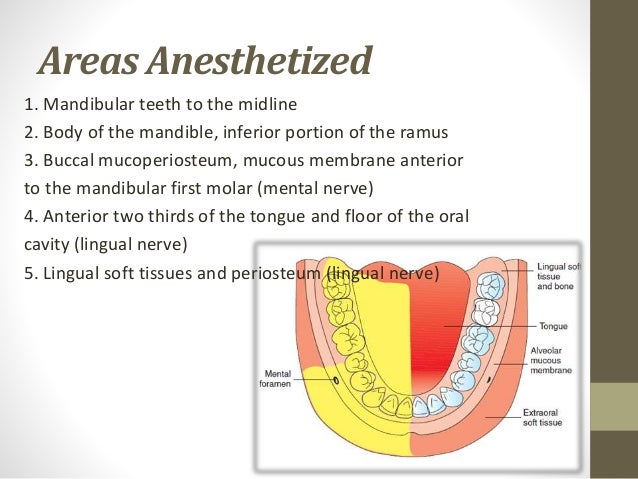
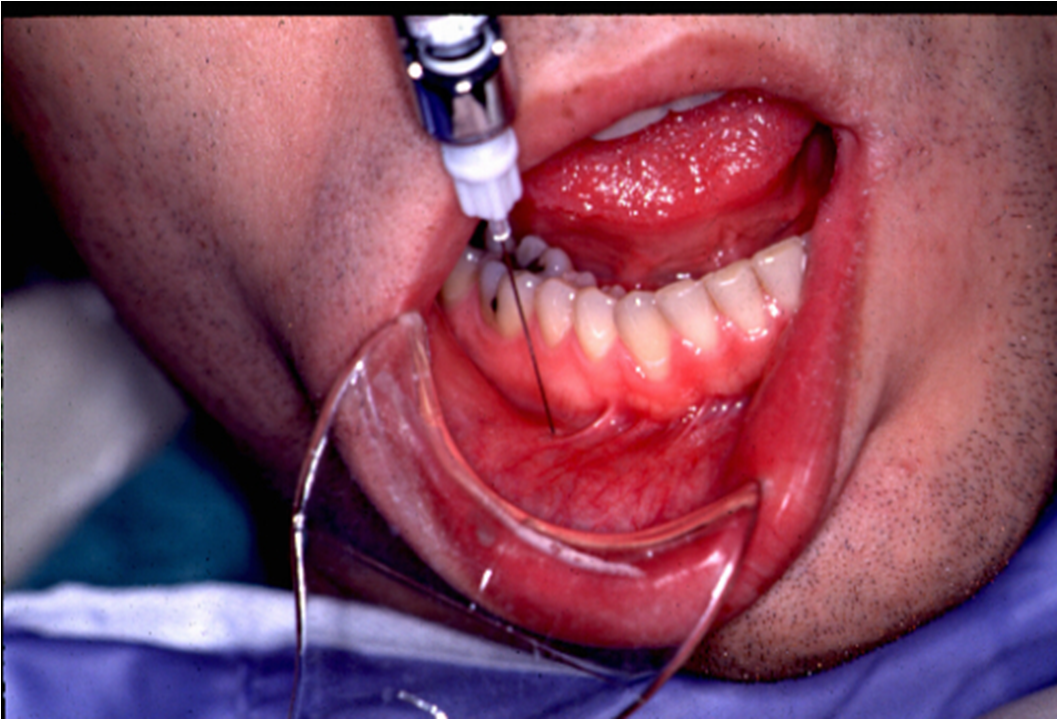
1. Inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB)
*Other name: Vazirani
*Numbness : Half of the mandible
*Once you need numbness of both side of mandible: Bilateral IANB
*Landmarkes & procedure:
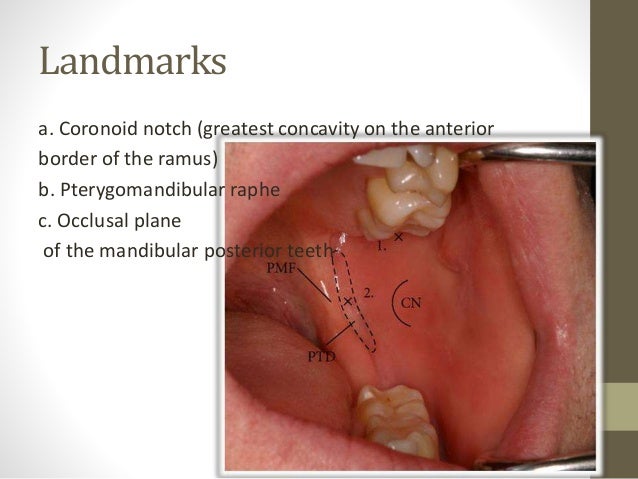
*Use Long needle 27 gauge
*Never use short needle for IAN BLOCK cause needle will break 
Needle should be at level of occlusal plane & between Lower 1st & 2nd PM .
For pediatric px needle should be above occlusal plane.
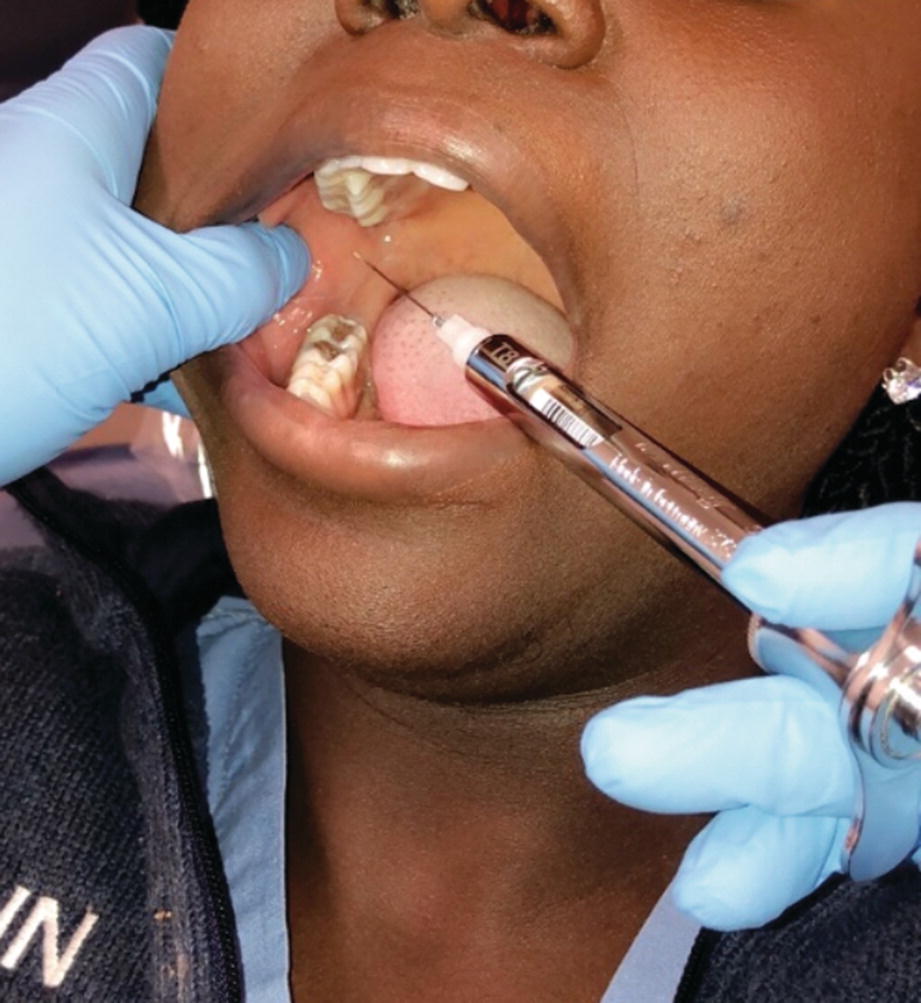
Slowly insert Half of the needle & heat the bone .
Change your neddle direction, Follow the central fossa of teeth & insert whole of the needle & Deposite the rest of the carpule.
*Example: Px came to your clinic for endo tx of tooth # 16. After Ian block & starting procedure, px is complaning of pain
1st complain : Proceed to Interligamentray anesthesia(Complement anesthesia for IAN) ; Bend the short 27 gauge needle by scoop technique & insert the needle 30 degree to interligument.
Anesthesia solution effects in interligament by passing PDL cell sheets(صفحات غربالی)

2nd complain: Intrapulpal anesthesia (secondary anesthesia); Bend the short 27 gauge needle by scoop technique & insert the needle 90 degree directly to the pulp.
*After IAN Block we proceed to Infiltration techmique for Reducing bleeding
2. Infiltration technique:
*Numbness: Soft tissue around the tooth & Dental plexus nerves
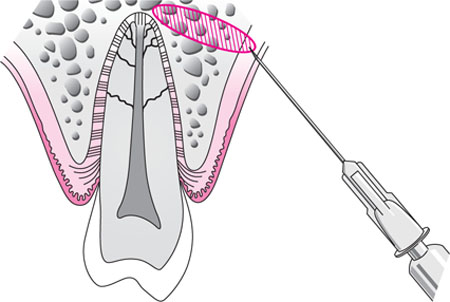
*Landmarkes & procedure:
On Labial or Buccal ,looks for Muccobual fold & Apex of root of the offending tooth.
On palatal, look for Gingival maring & Midline of the plate.
On Lingual, look for muco-lingual fold.
On Labial or Buccal, insert the needle 2mm away from the muccobucal fold at 45 degree till you heat the bone.
On palatal , insert the needle at 90 degree between Gingival maring & Midline of the plate.To achive this, the needle should derived from opposite side.
On Lingual, insert the needle above the muco-lingual fold to avoid dissemination of the solution into the floor of the mouth.
Deposite half of carpule on each side for 60 sec.
*Use 27 gauge short needle
3. Buccal nerve block
*Insert the needle parralel to occlusal plane, Distal to second molar.
*Use 27 gauge short needle with length of 20 mm (1.0 inch) .
*Deposit about 1 ml of solution around the inferior alveolar nerve.

4. Mental nerve block:
*Landmarkes:
Retract the cheek and lip & locate the junction of mandibular 1st &2nd premolars & down 1 cm inferior to the gum line (just medial to the midline pupil)
*Insert the needle Distal to second premolar.
*Use 27 gauge short needle.
*Deposit one third to one half of the cartridge.
*The difference between the mental nerve block & the incisive nerve block is that the incisive nerve block requires pressure to the mental foramen.
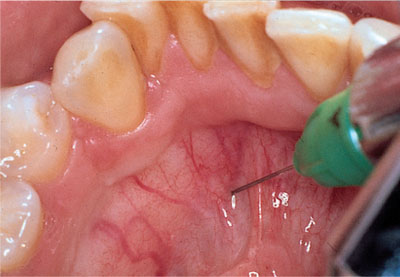
5. Incisive nerve block:
*This technique is painful and not used routinely especially for the pediatric patient
*Landmarkes & procedure:
Palatal mucosa just lateral to the incisive papilla (located in the midline behind the central incisors).
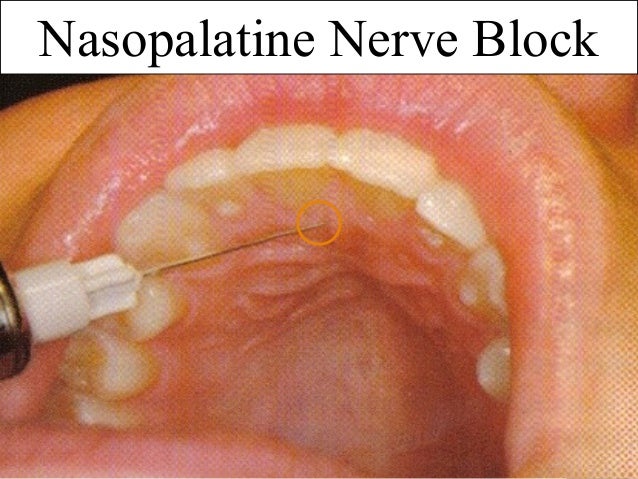
*Use 27 gauge short needle.
Insert the needle approaching incisive papilla at a 45 degree.
Place the cotton applicator directly onto the incisive papilla & Apply sufficient pressure so there is blanching.
Place the bevel of the needle against the blanched soft tissue at the injection site.
Apply enough pressure to slightly bow the needle.
Deposit a small amount of anesthetic; Straighten the needle and penetrate the tissue with the needle & Continue to apply pressure with the cotton applicator while injecting until bone is contacted (about 5mm).
Deposit no more than a ¼ cartridge.
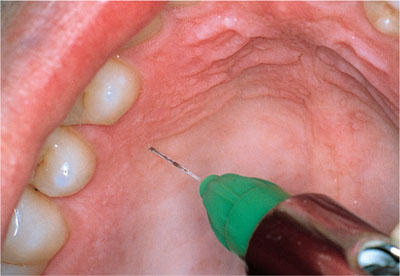
6. Greater palatine nerve block
* It is less traumatic than the nasopalatine nerve block because the palatal tissue in the area of the injection site is not as anchored to the underlying bone
*Landmarkes & procedure:
Maxillary first molar (or second primary molar in the primary dentition)

First Place a cotton swab at the junction of the hard palate and the maxillary alveolar process.
Apply pressure with the cotton swab while moving posteriorly.
The cotton swab on will fall into the depression created by the greater palatine foramen.
Move the cotton swabr posteriorly so it is directly over the greater palatine foramen and apply sufficient pressure to blanch the tissue for 30 seconds
Direct the syringe into the mouth from the opposite side of the mouth from the injection site at a 90 degree
Deposit a small volume of anesthetic( Straighten the needle and allow the needle to penetrate the mucosa, while depositing)
Slowly advance the needle approximately 8mm until palatine bone is contacted.
Deposite ¼ cartridge of anesthetic solution over 30 seconds.

Reference:
https://www.dentalcare.com/en-us
Lecture of Dr jimmy Aldecua & Dr Rea Corpuz at national university college of dentistry- manila, philippines
برچسبها: Surgery
کتاب وحتی یک کلمه هم نگفت
نگاهم به نوشته ای افتاد "پدر به تو کمک خواهد کرد"
چشمهایم را بستم، کلمه ی پدر در من ماند، اول آشکارا به شکل یک نوشته، سه حرفش پشت پلکهای بسته ام ایستادند ومحو شدند.
کلمه ی پدر در من فرورفت و به نظر میرسید همینطور پایین تر میرفت، هیچ جا متوقف نشد و ناگهان دوباره در درونم بالا آمد و قلبم را در نور دید، در رگهایم انباشته شد و مثل خون جریان یافت و به طرز وحشتناکی احساس دلتنگی کردم اما دوباره نسبت به همه ی این چیزها بی تفاوت شدم.

برچسبها: شخصی
کتاب موش ها و آدم ها
لِنی، مردی درشت هیکل و کودنی بود واز نوازش چیزهای نرم لذت میبرد ولی به خاطر ظاهرش فقط موش و سگ، برای نوازش نصیبش میشد.
با دستانِ زمختش سر آنها را به آرامی نوازش میکرد،کم کم دستش رامحکمتر میکشید و میگفت چقدر لطیف! حیوان ازدرد تقلا میکرد ولی لِنی با دستانش سعی در ساکت کردنش داشت،وقتی دستش را برمیداشت که حیوان بی حرکت بود.
لِنی از ازاینکه دیگران ممکن است اورا دعوا کنند، عصبانی میشد و جنازه را با عصبانیت به طرفی پرت میکرد و داد میزد چرا مُردی؟

برچسبها: شخصی
کتاب عقد و داستان های دیگر
چه کسی زندگی را تعریف کرده است؟
داستانی که نویسنده ای مینویسد ولی خوانده نمیشود یا ترانه ای که نوازنده ی خام دستی میزند ولی به دل نمی نشیند.

برچسبها: شخصی
کتاب بوف کور
و من فهمیدم تا ممکن است باید خاموش شد،تا ممکن است باید افکارخودم را برای خودم نگه دارم.

برچسبها: شخصی
